因为是即时写的,所以没考虑到合约漏洞的复杂性和其他问题,导致本文的合约过于简单,所以后续再换其他的漏洞合约,具有参考价值的
所以本篇暂时烂尾,有时间再换
写在前面 审计工具 在对合约进行审计的过程中,可以使用多种工具来辅助,而不是干看代码。
同我们对比如php,java等语言进行debug不同,solidity的传输都是以字节码来展现的。
不过我们依然有多种办法进行debug。
比如:
Remix:http://remix.ethereum.org/ 但是非常鸡肋,大部分的操作都不能完成,并且显示的是字节码。
我们可以使用一些框架
比如个人喜欢foundry 可以结合很多种分析工具,比如:slither mythril
在代码审计过程中,我们不用所谓的debug而是test。它有多种含义。
我们可以fork到本地进行测试审计,比如使用foundry/hardhat + Ganache
当然我比较喜欢的是使用https://blocksec.com/fork https://www.buildbear.io/ 不同于打印log更喜欢直接…
一些分析工具:
https://blocksec.com/phalcon
https://dashboard.tenderly.co/explorer
https://ethtx.info/
https://openchain.xyz/trace
https://evm.storage/
发现 当收到了漏洞合约攻击事件,我们可以进行狩猎追踪。
很多代币都是直接copy的,我们进行扫块,这点就不用说了。
当然还有更为简便的方法比如查找相似合约,
https://etherscan.io/find-similar-contracts
https://bscscan.com/find-similar-contracts
https://polygonscan.com/find-similar-contracts
…
在之前的一次漏洞中,我们使用了这种方法,可以写一个爬虫去获取列表并且对比漏洞合约。
或者进行扫块,但是扫块需要节点或者付费购买节点服务,比如All That Node alchemy
及时利用,更灵活,比区块浏览器查到的更多
https://dune.com/home
合约审计 这里我们随便找一个受攻击合约,比如Z123。对已知漏洞合约测试。自己在测试时同理。
(这个漏洞我开始看了才发现很简单,就是一个调用问题)
合约地址:0xb000f121A173D7Dd638bb080fEe669a2F3Af9760
https://bscscan.com/token/0xb000f121a173d7dd638bb080fee669a2f3af9760
这里我们以foundry来测试。
最新版本可以clone合约,只需要在.env中配置即可
在foundry.toml中修改合约版本
1 2 [settings] solc_version = "0.5.0"
首先需要先fork网络,方便后续操作。
只需要在.env或者foundry.toml中添加rpc即可,我这里先添加公开rpc
1 2 [rpc_endpoints] bsc = "https://rpc.ankr.com/bsc"
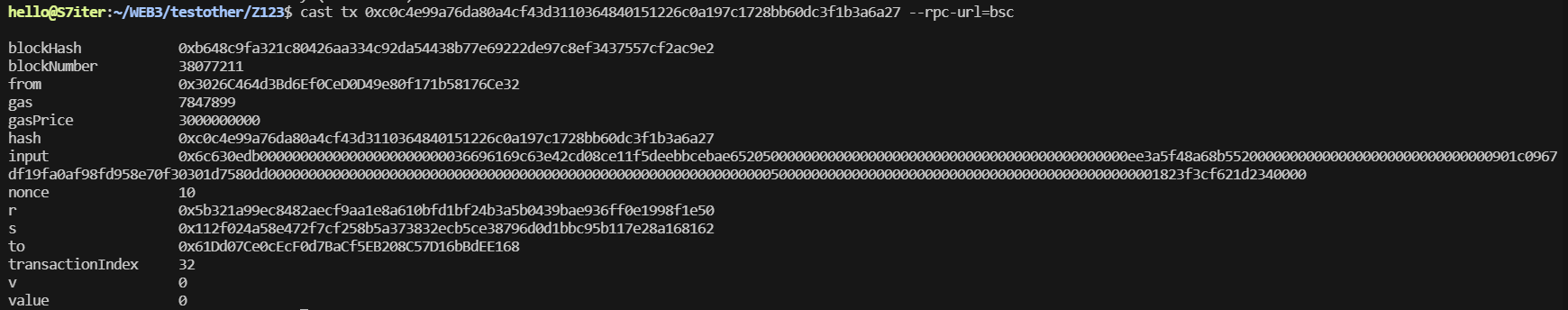
当出现如下,说明测试环境已经可以了
1 cast tx 0xc0c4e99a76da80a4cf43d3110364840151226c0a197c1728bb60dc3f1b3a6a27 --rpc-url=bsc
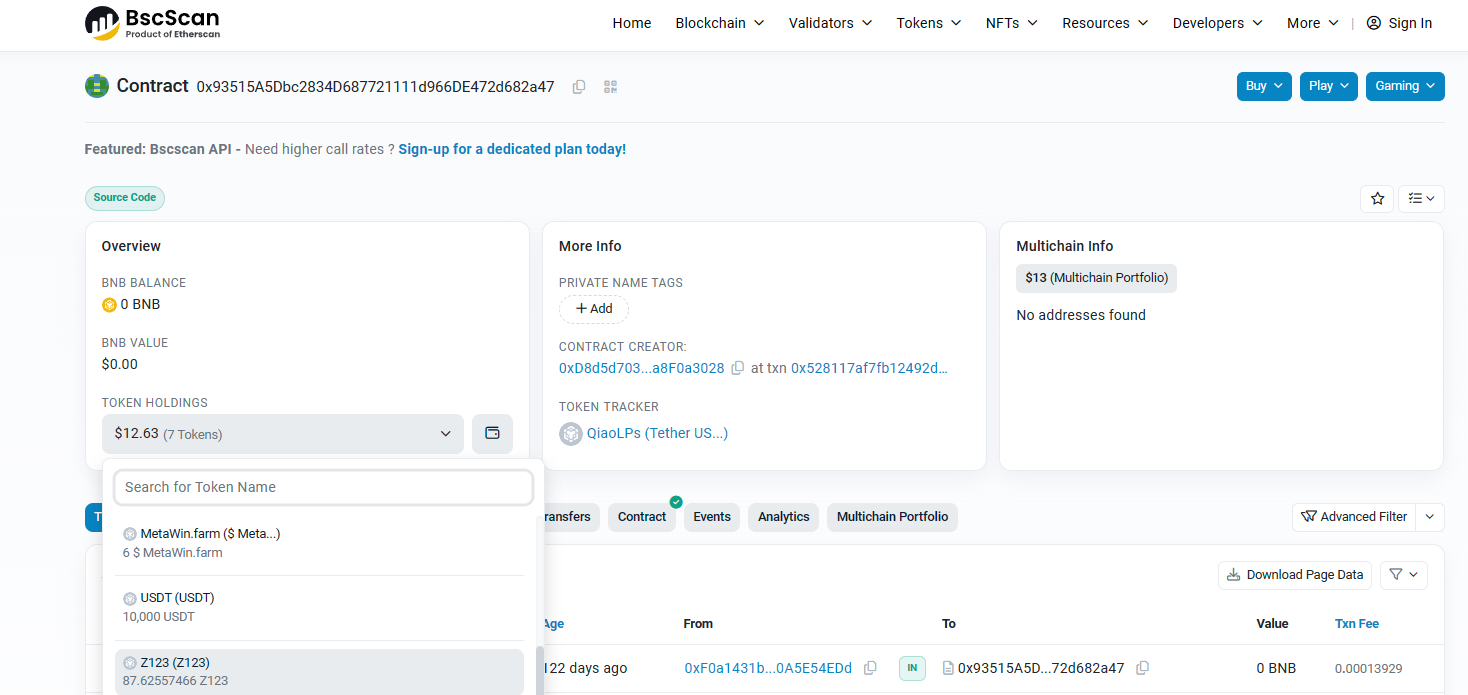
这是受攻击tx。如果我们是对此项目第一次审计。我们可以查找其他的交易tx,可以很容易找到QiaoLP
https://bscscan.com/address/0x93515a5dbc2834d687721111d966de472d682a47
我们继续对此攻击tx进行分析:
https://app.blocksec.com/explorer/tx/bsc/0xc0c4e99a76da80a4cf43d3110364840151226c0a197c1728bb60dc3f1b3a6a27
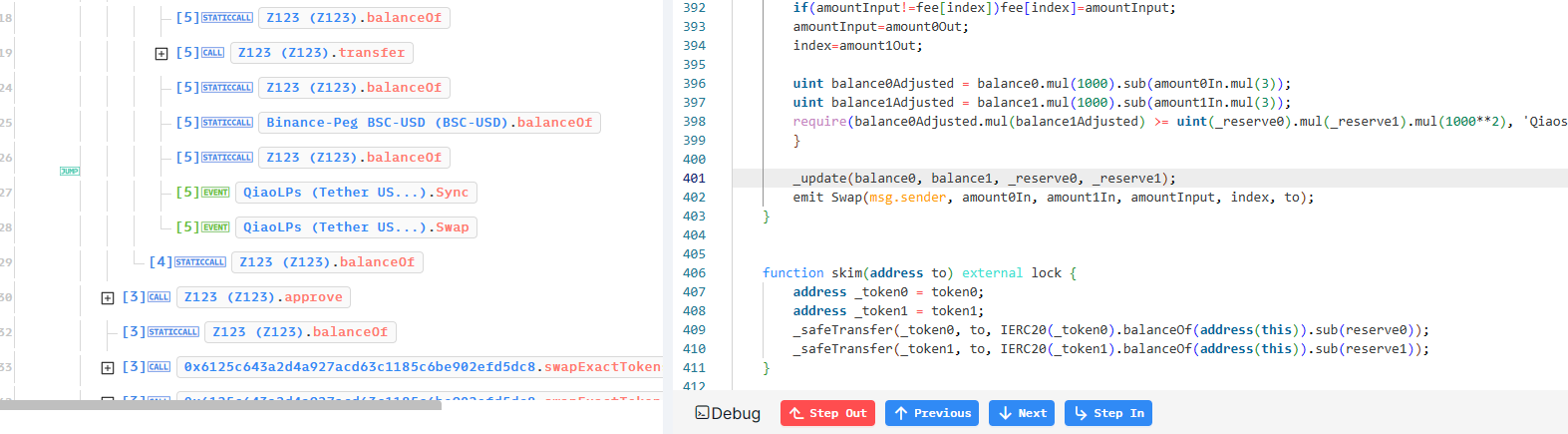
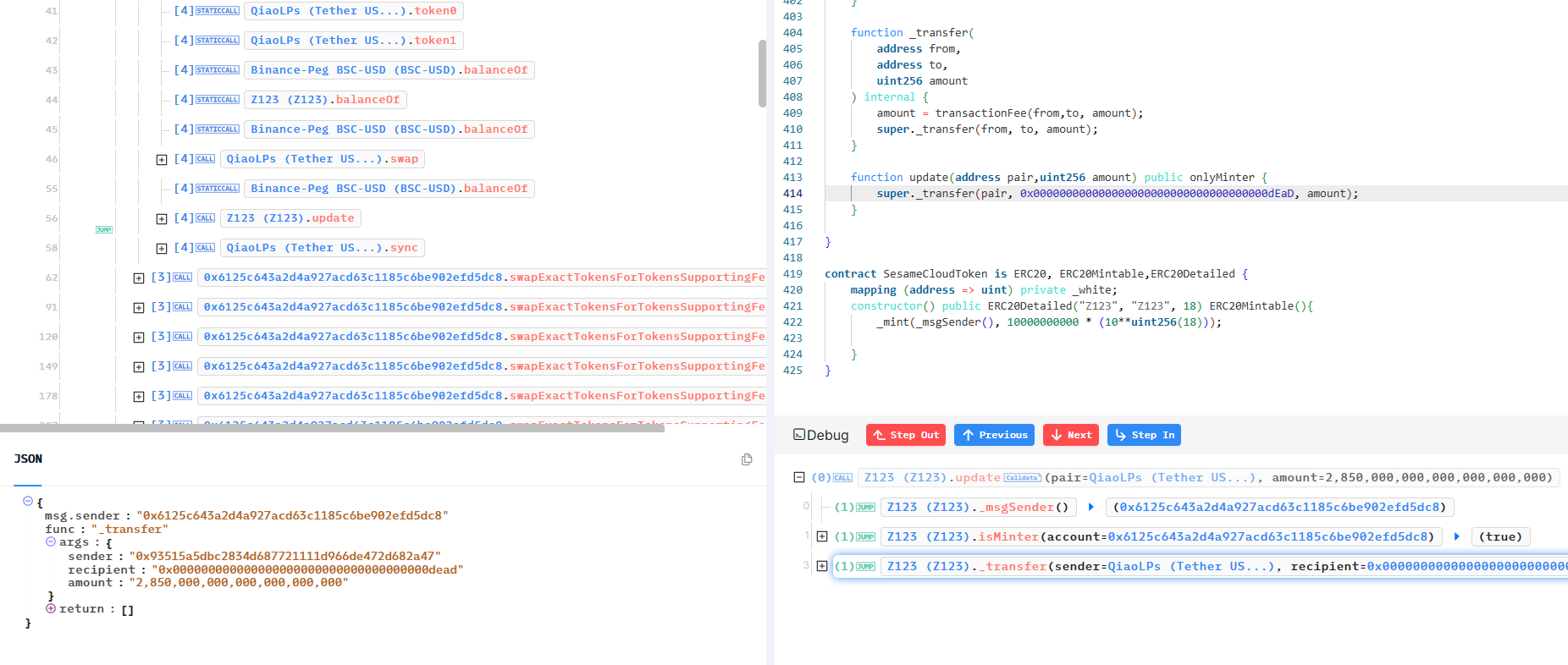
我们不难发现,通过0x6125c合约,其实也就是QianLp合约可以调用Z123合约的update函数,可以将QianLP对中的对应代币进行了销毁.
1 2 3 function update (address pair ,uint256 amount) public onlyMinter { super._transfer(pair , 0x000000000000000000000000000000000000dEaD , amount); }
这其实是一个错误的调用规则。我们可以看到,黑客通过路由器合约调用了update,
在路由器合约代码中:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 function swap (uint amount0Out, uint amount1Out, address to,uint amountInput, bytes calldata data) external lock { require (amount0Out > 0 || amount1Out > 0 , 'QiaoswapV2 : INSUFFICIENT_OUTPUT_AMOUNT'); (uint112 _reserve0, uint112 _reserve1,) = getReserves (); require (amount0Out < _reserve0 && amount1Out < _reserve1, 'QiaoswapV2 : INSUFFICIENT_LIQUIDITY'); uint balance0; uint balance1; uint index; { address _token0 = token0; address _token1 = token1; require (to != _token0 && to != _token1, 'QiaoswapV2 : INVALID_TO'); if (amount0Out > 0 ) { expend (amount0Out,index,_token0,to); } if (amount1Out > 0 ) { index=1 ; expend (amount1Out,index,_token1,to); } if (data.length > 0 ) IQiaoswapV2Callee (to).QiaoswapV2Call (msg.sender, amount0Out, amount1Out, data); balance0 = IERC20 (_token0).balanceOf (address (this)); balance1 = IERC20 (_token1).balanceOf (address (this)); } uint amount0In = balance0 > _reserve0 - amount0Out ? balance0 - (_reserve0 - amount0Out) : 0 ; uint amount1In = balance1 > _reserve1 - amount1Out ? balance1 - (_reserve1 - amount1Out) : 0 ; require (amount0In > 0 || amount1In > 0 , 'QiaoswapV2 : INSUFFICIENT_INPUT_AMOUNT'); { uint input=(amount0In>0 ?amount0In:amount1In).mul (1000 ); amountInput=input.div (amountInput); if (amountInput!=fee[index])fee[index]=amountInput; amountInput=amount0Out; index=amount1Out; uint balance0Adjusted = balance0.mul (1000 ).sub (amount0In.mul (3 )); uint balance1Adjusted = balance1.mul (1000 ).sub (amount1In.mul (3 )); require (balance0Adjusted.mul (balance1Adjusted) >= uint (_reserve0).mul (_reserve1).mul (1000 **2 ), 'QiaoswapV2 : K'); } _update(balance0, balance1, _reserve0, _reserve1); emit Swap (msg.sender, amount0In, amount1In, amountInput, index, to); }
虽然使用了external我们无法进行内部调用,但是我们可以发现
调用了_update。每次当路由器合约swap被调用时,就会用调用Z123代币合约的update
根据代码可以明显看到:
代币合约(SesameCloudToken)继承了ERC20Mintable合约
ERC20Mintable合约中有一个update函数,可以销毁指定地址上的Token余额
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 contract ERC20Mintable is ERC20, MinterRole { using SafeMath for uint256 ; using Address for address ; uint[] public _transactFeeValue=[5 ,10 ,50 ]; uint public sale_date=1695069060 ; uint256[][] private ContractorsFee; address[][] private ContractorsAddress; mapping (address => uint) private _white; function update (address pair,uint256 amount) public onlyMinter { super ._transfer(pair, 0x000000000000000000000000000000000000dEaD , amount); } } contract SesameCloudToken is ERC20, ERC20Mintable,ERC20Detailed { mapping (address => uint) private _white; constructor () public ERC20Detailed ("Z123" , "Z123" , 18 ) ERC20Mintable (){ _mint(_msgSender(), 10000000000 * (10 **uint256 (18 ))); }
所以追溯下来就是:如果攻击者可以控制路由合约swap函数中的to参数,就可以将销毁Token的地址设置为正常交易对的pair地址,从而通过调用swap来销毁该交易对的Token余额。
对于获利方式我们可以这样理解:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 假设黑客有 1000 USDT。他们使用路由器合约将 1000 USDT 换成 Z123。 1000 USDT -> 100 Z123 现在,黑客拥有 100 个 Z123。他们使用路由器合约调用 update 函数销毁货币对中的一半代币。 update(lp, 50) 这将销毁流动性池中 50 个 Z123,只剩下 50 个 Z123。这导致 Z123 的价格上涨。 黑客现在将剩余的 50 个 Z123 换成 USDT。 50 Z123 -> 1100 USDT 黑客现在拥有 1100 USDT。他们通过销毁货币对中的一半代币,使 Z123 的价格上涨,从而获利。
链上分析:https://app.blocksec.com/explorer/tx/bsc/0xc0c4e99a76da80a4cf43d3110364840151226c0a197c1728bb60dc3f1b3a6a27
攻击者地址:https://bscscan.com/address/0x3026c464d3bd6ef0ced0d49e80f171b58176ce32
QianLP合约地址:https://bscscan.com/address/0x6125c643a2d4a927acd63c1185c6be902efd5dc8
https://bscscan.com/address/0x901c0967df19fa0af98fd958e70f30301d7580dd …
现在让我们使用foundry测试和复现
测试和复现 我们可以先对函数进行test,
我们可以编写测试,了解调用关系。
(因为漏洞合约版本太低,找了很多方法都没解决,等有机会用hardhat再写一次)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 hello@S7iter:~/WEB3/testother/Z123$ forge test 2024-04-25T09:09:55.927926Z ERROR foundry_compilers::resolver: failed to resolve versions Error: Found incompatible Solidity versions: test/exp.t.sol (<0.5.0) imports: lib/forge-std/src/Test.sol (>=0.6.2 <0.9.0) src/Z123.sol (>=0.5.0) src/QiaoLp.sol (=0.5.16) lib/forge-std/src/console.sol (>=0.4.22 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/console2.sol (>=0.4.22 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/safeconsole.sol (>=0.6.2 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/StdAssertions.sol (>=0.6.2 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/StdChains.sol (>=0.6.2 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/StdCheats.sol (>=0.6.2 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/StdError.sol (>=0.6.2 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/StdInvariant.sol (>=0.6.2 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/StdJson.sol (>=0.6.0 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/StdMath.sol (>=0.6.2 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/StdStorage.sol (>=0.6.2 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/StdStyle.sol (>=0.4.22 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/StdToml.sol (>=0.6.0 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/StdUtils.sol (>=0.6.2 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/Vm.sol (>=0.6.2 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/Base.sol (>=0.6.2 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/Vm.sol (>=0.6.2 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/Vm.sol (>=0.6.2 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/StdStorage.sol (>=0.6.2 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/console2.sol (>=0.4.22 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/Vm.sol (>=0.6.2 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/Vm.sol (>=0.6.2 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/Vm.sol (>=0.6.2 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/Vm.sol (>=0.6.2 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/Vm.sol (>=0.6.2 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/interfaces/IMulticall3.sol (>=0.6.2 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/mocks/MockERC20.sol (>=0.6.2 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/mocks/MockERC721.sol (>=0.6.2 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/Vm.sol (>=0.6.2 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/StdStorage.sol (>=0.6.2 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/Vm.sol (>=0.6.2 <0.9.0) lib/forge-std/src/interfaces/IERC20.sol (>=0.6.2) lib/forge-std/src/interfaces/IERC721.sol (>=0.6.2) lib/forge-std/src/interfaces/IERC165.sol (>=0.6.2)